The Assassination of Archduke Shinzo Abe
When the Globalists Crossed the Rubicon
by Emanuel Pastreich, Fear No Evil
July 14, 2022
July 8 was a muggy day in the ancient capital of Japan. Shinzo Abe, the most powerful figure in Japanese politics, was delivering a stump speech for a local Liberal Democratic Party candidate in front of the Nara Kintetsu railway station when suddenly a loud bang rang out, followed by an odd cloud of smoke.
The response was incredible. Among those in the unusually large crowd gathered, not a single person ran for cover, or hit the ground in terror.
Abe’s body guards, who stood unusually far away from him during the speech, looked on impassively, making no effort to shield him, or to pull him to a safe location.
A few seconds later, Abe crumpled and collapsed to the ground, lying there impassive in his standard blue jacket, white shirt, now speckled with blood, and trademark blue badge of solidarity with Japanese abductees in North Korea. Most likely he was killed instantaneously.
Only then did the body guards seize the suspect, Yamagami Toruya, who was standing behind Abe. The tussle with Yamagami took the form of a choreographed dance for the television audience, not a professional takedown.
Yamagami was immediately identified by the media as a 41-year-old former member of the Maritime Self-Defense Force who had personal grievances with Abe.
Yamagami told everything to the police without hesitation. He did not even try to run from the scene and was still holding the silly hand-made gun when the bodyguards grabbed him.
Even after Abe was lying on the pavement, not a single person in the crowd ran for shelter, or even looked around to determine where the shots came from. Everyone seemed to know, magically, that the shooting was over.
Then the comedy began. Rather than putting Abe in a limousine and whisking him away, those standing around him merely called out to passersby, asking if anyone was a doctor.
The media immediately embraced the “lone gunman” conclusion for this attack, repeating entertaining tale of how Yamagami was associated with Toitsu Kyokai, a new religion started by the charismatic shaman Kawase Kayo, and why he blamed Abe, who had exchanges with that group, for his mother’s troubles.
Because Toitsu Kyokai has followers from the Unification Church founded by Reverend Moon Sun Myung, journalist Michael Penn jumped to the conclusion that the conspiracy leading to Abe’s death was the result of his collaboration with the Moonies.
Although the mainstream media accepted this fantastic story, the Japanese police and security apparatus did not manage to squash alternative interpretations. Blogger Takashi Kitagawa posted materials on July 10 that suggested Abe was shot from the front, not from the back where Yamagami stood, and that the shots must have been fired at an angle from the top of one, or both, of the tall buildings on either side of the intersection across from the railway station plaza.
Takahashi Kitakawa’s postings:

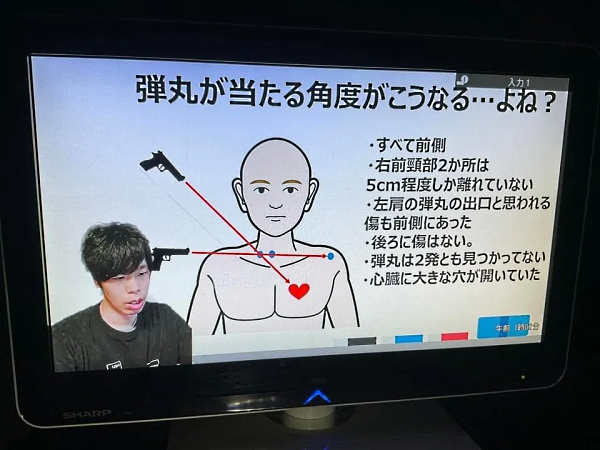
Kitagawa’s analysis of the paths of the bullets was more scientific than anything offered by the media that had claimed, without basis, that Abe had only been shot once until the surgeon announced that evening that there had been two bullets.
The chances that a man holding an awkward home-made gun, standing more than five meters away in a crowd, would be able to hit Abe twice are low. The TV personality Kozono Hiromi, who is a gun expert himself, remarked on his show “Sukkiri” (on July 12) that such a feat would be incredible.
A careful viewing of the videos suggests that multiple shots were fired by a rifle with a silencer from atop a neighboring building.
The message to the world
For a figure like Shinzo Abe, the most powerful political player in Japan and the person to whom Japanese politicians and bureaucrats rallied in response to the unprecedented uncertainty born of the current geopolitical crisis, to be shot dead with no serious security detail nearby makes no sense.
Perhaps the message was lost on viewers at home, but it was crystal clear for other Japanese politicians. For that matter, the message was clear for Boris Johnson, who was forced out of power at almost exactly the same moment that Abe was shot, or for Emanuel Macron, who was suddenly charged with influence peddling scandal for Uber, and faces demands for his removal from office, on July 11—after months of massive protests had failed to sway him in any way.
The message was written all over Abe’s white shirt in red: buying into the globalist system and promoting the COVID-19 regime is not enough to assure safety, even for the leader of a G7 nation.
Abe was highest ranking victim so far of the hidden cancer eating away at governance in nation states around the world, an institutional sickness that moves decision making away from national governments to a network of privately-held supercomputer banks, private equity groups, for-hire intelligence firms in Tel Aviv, London and Reston, and the strategic thinkers employed by the billionaires at the World Economic Forum, NATO, the World Bank and other such awesome institutions.
The fourth industrial revolution was the excuse employed to transfer the control of all information in, and all information out, for central governments to Facebook, Amazon, Oracle, Google, SAP and others in the name of efficiency. As J. P. Morgan remarked, “Everything has two reasons: a good reason and a real reason.”
With the assassination of Abe, these technology tyrants, and their masters, have crossed the Rubicon, declaring that those dressed in the trappings of state authority can be mowed down with impunity if they do not follow orders.
The Problem with Japan
Japan is heralded as the only Asian nation advanced enough to join the “West,” to be a member of the exclusive G7 club, and to be qualified to enter into collaboration with (and possible membership in) the top intelligence sharing program, the “Five Eyes.” Nevertheless, Japan has continued to defy the expectations, and the demands, of global financiers, and the planners within the beltway and on Wall Street for the New World Order.
Although it was South Korea in Asia that has constantly been berated in Washington as an ally not quite up to the level of Japan, the truth is that the super-rich busy taking over the Pentagon, and the entire global economy, were starting to harbor doubts about the dependability of Japan.
The globalist system at the World Bank, Goldman Sachs, or the Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs at Harvard University has a set track for the best and the brightest from “advanced nations.”
Elites from Australia, France, Germany, Norway or Italy, learn to speak fluent English, spend time in Washington, London, or Geneva at a think tank or university, secure a safe sinecure at a bank, a government institution, or a research institute that assures them a good income, and adopt the common sense, pro-finance, perspective offered by the Economist Magazine as the gospel.
Japan, however, although it has an advanced banking system of its own, although its command of advanced technologies makes it the sole rival of Germany in machine tools, and although it has a sophisticated educational system capable of producing numerous Nobel Prize winners, does not produce leaders who follow this model for the “developed” nation.
Japanese elite do not study abroad for the most part and Japan has sophisticated intellectual circles that do not rely on information brought in from overseas academic or journalistic sources.
Unlike other nations, Japanese write sophisticated journal articles entirely in Japanese, citing only Japanese experts. In fact, in fields like botany and cellular biology, Japan has world-class journals written entirely in Japanese.
Similarly, Japan has a sophisticated domestic economy that is not easily penetrated by multinational corporations—try as they do.
The massive concentration of wealth over the last decade has allowed the super-rich to create invisible networks for secret global governance,best represented by the World Economic Forum’s Young Global Leaders program and the Schwarzman Scholars program. These rising figures in policy infiltrate the governments, the industries, and research institutions of nations to make sure that the globalist agenda goes forth unimpeded.
Japan has been impacted by this sly form of global governance. And yet, Japanese who speak English well, or who study at Harvard, are not necessarily on the fast track in Japanese society.
There is stubborn independence in Japan’s diplomacy and economics, something that raised concerns among the Davos crowd during the COVID-19 campaigns.
Although the Abe administration (and the subsequent Kishida administration) went along with the directives of the World Economic Forum and the World Health Organization for vaccines and social distancing, the Japanese government was less intrusive in the lives of citizens than most nations, and was less successful in forcing organizations to require vaccination.
The use of QR codes to block service to the unvaccinated was limited in its implementation in Japan in comparison with other “advanced” nations.
Moreover, the Japanese government refuses to fully implement the digitalization agenda demanded, thus denying multinational technology giants the control over Japan that they exercise elsewhere. This lag in Japan’s digitalization led the Wilson Center in Washington D.C. to invite Karen Makishima, minister of Japan’s Digital Agency (launched under pressure from global finance in September, 2021) so that she could explain why Japan has been so slow to digitalize (July 13).
Japanese are increasingly aware that their resistance to digitalization, to the wholescale outsourcing of the functions of government and university to multinational tech giants, and the privatization of information, is not in their interest.
Japan continues to operate Japanese-language institutions that follow old customs, including the use of written records. Japanese still read books and they are not so enamored with AI as Koreans and Chinese.
Japan’s resistance can be traced back to Meiji restoration of 1867. Japan set out to create governmental system wherein Western ideas were translated into Japanese, combined with Japanese concepts, to create a complex domestic discourse. The governance system set up in Meiji restoration remains in place to a large degree, using models for governance based on pre-modern principles from Japan and China’s past, and drawn from 19th century Prussia and England.
The result is feudalistic approach to governance wherein ministers oversee fiefdoms of bureaucrats who carefully guard their own budgets and who maintain their own internal chains of command.
The Problem with Abe
Shinzo Abe was one of the most sophisticated politicians of our age, always open to make a deal with the United States, or other global institutions, but always cagy when it came to making Japan the subject of globalist dictates.
Abe harbored the dream of restoring Japan to its status as an empire, and imagined himself to be the reincarnation of the Meiji Emperor.
Abe was different than Johnson or Macron in that he was not as interested in appearing on TV as he was in controlling the actual decision making process within Japan.
There is no need to glorify Abe’s reign, as some have tried to do. He was a corrupt insider who pushed for the dangerous privatization of government, the hollowing out of education, and who backed a massive shift of assets from the middle class to the wealthy.
His use of the ultra-right Nihon Kaigi forum to promote an ultranationalist agenda, and to glorify the most offensive aspects of Japan’s imperial past, was deeply disturbing. Abe gave his unflinching support for all military expenditures, no matter how foolish, and he was willing to support just about any American boondoggle.
That said, as the grandson of Prime Minister Nobusuke Kishi, and the son of foreign minister Shintaro Abe, Shinzo Abe showed himself to be an astute politician from childhood. He was creative in his use of a wide range of political tools to advance his agenda, and he could call on corporate and government leaders from around the world with an ease that no other Asian politician could.
I remember vividly the impression I received from Abe on the two occasions that I met him in person. Whatever cynical politics he may have promoted, he radiated to his audience a purity and simplicity, what the Japanese call “sunao,” that was captivating. His manner suggested a receptiveness and openness that inspired loyalty among his followers and that could overwhelm those who were hostile to his policies.
In sum, Abe was sophisticated political figure who was capable of playing one side against the other within the Liberal Democratic Party, and within the international community, while appearing to be a considerate and benevolent leader.
For this reason, Japanese hostile to Abe’s ethnic nationalism were still willing to support him because he was the only politician they thought capable of restoring global political leadership to Japan.
Japanese diplomats and military officers fret endlessly about the Japan’s lack of vision. Although Japan has all the qualifications to be a great power, they reason, it is run by a series of unimpressive, University of Tokyo graduates; men who are good at taking tests, but are unwilling to take risks.
Japan produces noone like Putin or Xi, and not even a Macron or a Johnson.
Abe wanted to be a leader and he had the connections, the talent, and the ruthlessness required to play that role on the global stage. He was already the longest serving prime minister in Japanese history, and had plans for a third bid as prime minister, when he was struck down.
Needless to say, the powers behind the World Economic Forum do not want national leaders like Abe, even if they conform with the global agenda, because they are capable of organizing resistance within the nation state.
What went wrong?
Abe was able to handle, using the traditional tools of statecraft, the impossible dilemma faced by Japan over the last decade as its economic ties with China and Russia increased, but its political and security integration with the United States, Israel and the NATO block proceeded apace.
It was impossible for Japan to be that close to the United States and its allies while maintaining friendly relations with Russia and China. Yet Abe almost succeeded.
Abe remained focused and cool. He made use of all his skills and connections as he set out to carve a unique space for Japan. Along the way, Abe turned to the sophisticated diplomacy of his strategic thinker Shotaro Yachi of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs to assure that Japan found its place under the sun.
Abe and Yachi used contradictory, but effective, geopolitical strategies to engage both East and West, making ample use of secret diplomacy to seal long-term deals that put Japan back in the great powers game.
On the one hand, Abe presented to Obama and Trump a Japan that was willing to go further than South Korea, Australia or other India in backing Washington’s position. Abe was willing to suffer tremendous domestic criticism for his push for a remilitarization that fit the US plans for East Asia.
At the same time that he impressed Washington politicians with his gung-ho pro-American rhetoric, matched by the purchase of weapons systems, Abe also engaged China and Russia at the highest levels. That was no small feat, and involved sophisticated lobbying within the beltway, and in Beijing and Moscow.
In the case of Russia, Abe successfully negotiated a complex peace treaty with Russia in 2019 that would have normalized relations and solved the dispute concerning the Northern Territories (the Kuril Islands in Russian). He was able to secure energy contracts for Japanese firms and to find investment opportunities in Russia even as Washington ramped up the pressure on Tokyo for sanctions.
The journalist Tanaka Sakai notes that Abe was not banned from entering Russia after the Russian government banned all other representatives of the Japanese government from entry.
Abe also engaged China seriously, solidifying long-term institutional ties, and pursuing free trade agreement negotiations that reached a breakthrough in the fifteenth round of talks (April 9-12, 2019). Abe had ready access to leading Chinese politicians and he was considered by them to be reliable and predictable, even though his rhetoric was harshly anti-Chinese.
The critical event that likely triggered the process leading to Abe’s assassination was the NATO summit in Madrid (June 28-30).
The NATO summit was a moment when the hidden players behind the scenes laid down the law for the new global order. NATO is on a fast track to evolve beyond an alliance to defend Europe and to become an unaccountable military power, working with the Global Economic Forum, the billionaires and the bankers around the world, as a “world army,” functioning much as the British East India Company did in another era.
The decision to invite to the NATO summit the leaders of Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand was a critical part of this NATO transformation.
These four nations were invited to join in an unprecedented level of integration in security, including intelligence sharing (outsourcing to big tech multinationals), the use of advanced weapons systems (that must be administrated by the personnel of multinationals like Lockheed Martin), joint exercises (that set a precedent for an oppressive decision-making process), and other “collaborative” approaches that undermine the chain of command within the nation state.
When Kishida returned to Tokyo on July first, there can be no doubt that one of his first meetings was with Abe. Kishida explained to Abe the impossible conditions that the Biden administration had demanded of Japan.
The White House, by the way, is now entirely the tool of globalists like Victoria Nuland (Under Secretary of State for Political Affairs) and others trained by the Bush clan.
The demands made of Japan were suicidal in nature. Japan was to increase economic sanctions on Russia, to prepare for possible war with Russia, and to prepare for a war with China. Japan’s military, intelligence and diplomatic functions were to be transferred to the emerging blob of private contractors gathering for the feast around NATO.
We do not know what Abe did during the week before his death. Most likely he launched into a sophisticated political play, using of all his assets in Washington D.C., Beijing, and Moscow—as well as in Jerusalem, Berlin, and London, to come up with a multi-tiered response that would give the world the impression that Japan was behind Biden all the way, while Japan sought out a détente with China and Russia through the back door.
The problem with this response was that since other nations had been shut down, such a sophisticated play by Japan made it the only major nation with a semi-functional executive branch.
Abe’s death parallels closely that of Seoul’s mayor Park Won Sun, who went missing on July 9th, 2020, exactly two years before Abe’s assassination. Park took steps in Seoul City Hall to push back on the COVID-19 social distancing policies that were being imposed by the central government. His body was found the next day and the death was immediately ruled a suicide resulting from his distress over charges of sexual harassment by a colleague.
What to do now?
The danger of the current situation should not be underestimated. If an increasing number of Japanese come to perceive, as the journalist Tanaka Sakai suggests, that the United States destroyed their best hope for leadership, and that the globalists want Japan to make do with an unending series of weak-minded prime ministers who are dependent on Washington and other hidden players of the parasite class, such a development could bring about a complete break between Japan and the United States, leading to a political or military conflict.
It is telling that Michael Green, the top Japan hand in Washington D.C., did not write the initial tribute to Abe that was published on the homepage of CSIS (Center for Strategic and International Studies), his home institute.
Green, veteran of the Bush National Security Council and Henry A. Kissinger Chair of the Asia Program at CSIS, is the author of Line of Advantage: Japan’s Grand Strategy in the Era of Abe Shinzo. Green was a close associate of Abe, perhaps the closest of any American.
The tribute to Abe was drafted by Christopher Johnstone (the Japan chair at CSIS and former CIA officer). The weird choice suggests that the assassination is so sensitive that Green instinctively wished to avoid writing the initial response, leaving it to a professional operative.
For responsible intellectuals and citizens in Washington, Tokyo, or elsewhere, there is only one viable response to this murky assassination: a demand for an international scientific investigation.
Painful as that process might be, it will force us to face the reality of how our governments have been taken over by invisible powers.
If we fail to identify the true players behind the scenes, however, we may be led into a conflict in which the blame is projected onto heads of state and countries are forced into conflicts so as to hide the crimes of global finance.
The loss of control of the Japanese government over the military the last time can be attributed in part to the assassinations of prime minister Inukai Tsuyoshi on May 15, 1932 and of prime minister Saito Makoto on February 26, 1936.
But for the international community, the more relevant case is how the manipulations of an integrated global economy by the Rothschild, Warburg, and other banking interests created an environment wherein the tensions produced by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary on June 28, 1914 were funneled towards world war.
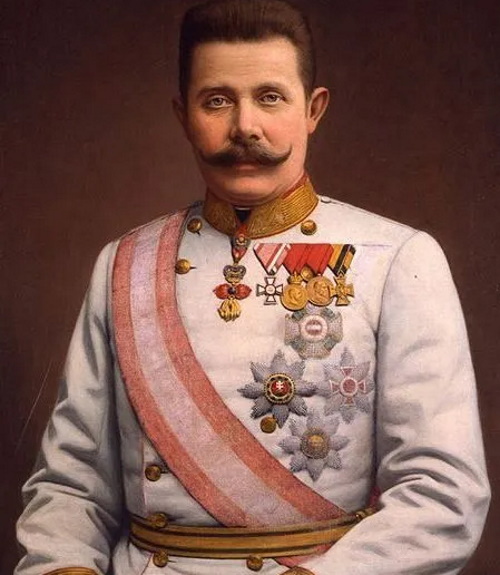
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914)

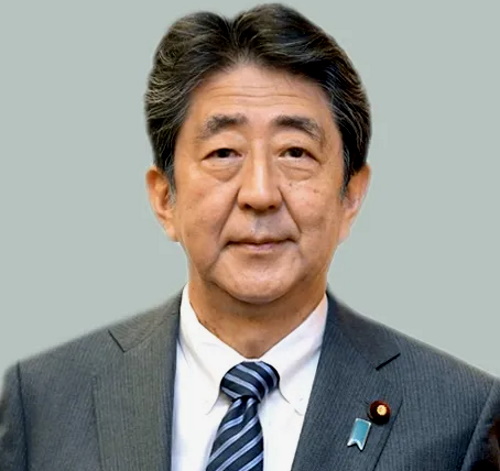
Shinzo Abe of Japan (21 September 1954 – 8 July 2022)

安倍晋三元総理大臣暗殺について 言明します from Emanuel Pastreich on Vimeo.
Connect with Emanuel Pastreich

Truth Comes to Light highlights writers and video creators who ask the difficult questions while sharing their unique insights and visions.
Everything posted on this site is done in the spirit of conversation. Please do your own research and trust yourself when reading and giving consideration to anything that appears here or anywhere else.










